JVM or Java Virtual Machine is an abstract platform-dependent virtual machine used by many JAVA Development Companies which provides a runtime environment in which java bytecode can be well-executed.
It is available for various hardware and software platforms and has a major role in carrying out modern-day innovations.
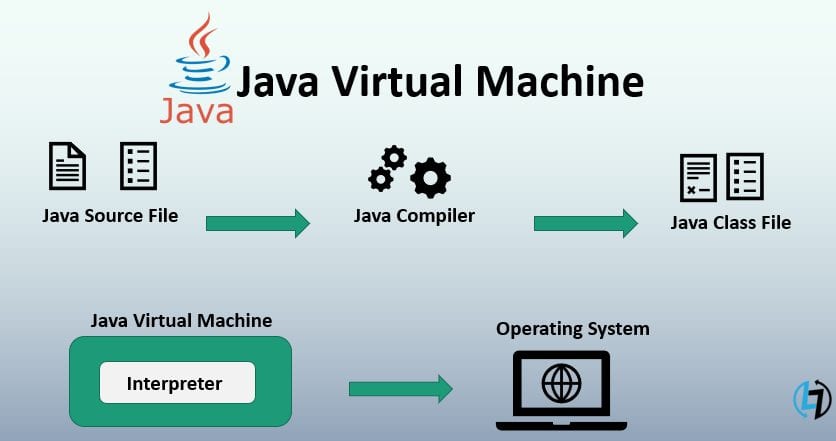
Function of a JVM
As discussed above it involves processes running on a machine, something similar to a server, which represents and controls the resource usage for a Java application. It, thus, basically performs 2 primordial functions – one, it works on the principle of “Write Once, Run Anywhere”, enabling the users to execute Java programs on nearly all devices and/or operating systems, and second, it optimizes and manages the program memory via a process known as Garbage Collection.
Besides, JVM also does tasks like loading the code, verifying it, executing it, and providing a suitable runtime environment to work efficiently. Not only this, but it also provides several definitions for different domains like class file format, register set, memory area, garbage-collected heap, fatal error reporting, etc..
Garbage Collection

It is a major process running within a JVM which involves continuous identification and removal of the memory which is currently not being put to use in a Java program and/or application.
Architecture of a JVM
It consists of various technically associated domains like:-
1. Classloader
Classloader is a subpart of JVM being used to load the class files. Whenever a java program is run, it is first loaded by the classloader and then accordingly executed. There are primarily three built-in internal classloaders in Java. However, others can also be created on the same lines. The 3 in-built classloaders include:-
A. Bootstrap ClassLoader
It is the first classloader which is a superclass of the Extension classloader works to loads the jar files, containing all class files of Java Standard Edition like java.net package classes, java.io package classes, java.util package classes, java.sql package classes, java.lang package classes etc…
B. Extension ClassLoader
This is a child classloader of the above mentioned and the parent classloader of the System classloader. It is responsible for loading the jar files located within $JAVA_HOME/JRE/lib/ext
C. System/Application ClassLoader
It is the child classloader of the above and deals with loading the class files from classpath.
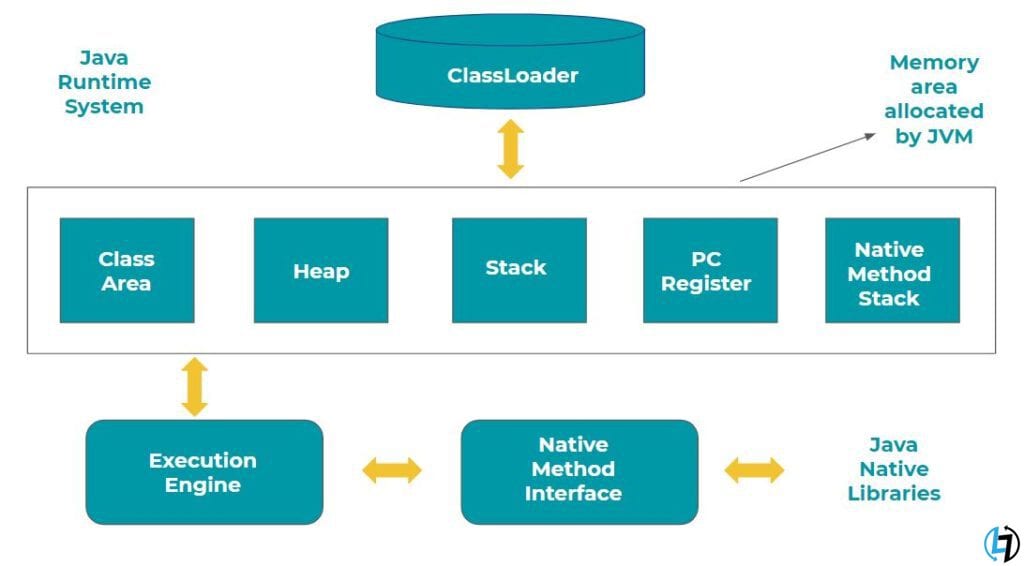
2. Class (Method) Area
Class (Method) Area stores per-class structures such as the field and method data, the runtime constant pool, the code for methods, etc…
3. Heap
It refers to the runtime data area where the allocation of objects takes place.
4. Stack
Storing of frames takes place, Java Stack. It holds local variables and partial results, thus playing an important part in the process of method invocation and return. Every thread has a private JVM stack which is created simultaneously along with the thread.
*A new frame is developed each time a method is invoked and is destroyed when the process of method invocation finishes.
5. Program Counter Register (PC)
PC (program counter) register has the address of the JVM instruction being executed currently.
6. Native Method Stack
It comprises of all the native methods being used in a program and/or an application.
7. Execution Engine
It includes: –
A. A virtual processor
B. Interpreter:
Executes the instructions reading the byte code stream.
C. Just-In-Time(JIT) compiler:
It is used as a tool to enhance the performance of a JVM and is responsible for compiling the parts of the bytecode that have similar functionalities at the same time, hence reducing the time required for the completion of the compilation process.
D. Java Native Interface:
Java Native Interface (JNI) is a framework providing a communication interface such that it can communicate with other applications other languages like C, C++, Assembly, etc. It is thus, also used to send output to the Console or interact with the OS libraries.
Working of a JVM
1. Loading
It refers to the cation of loading a/the file on the memory using the classloaders and then representing it in the heap memory.
2. Linking
It is a 3 fold process, involving –
-
Verification:
Ensures the correctness of .classfile, checking whether the file is formatted properly and whether or not is generated by a valid compiler. If verification fails, a run-time exception java.lang.VerifyError is given.
-
Preparation:
Allocates memory for class variables and initializes it to the default values.
-
Resolution:
Replaces symbolic references with direct references, by searching into the method area so as to locate the entity being referred to.
3. Initialization
Under this process, all the static variables are assigned their respective values as defined in the code and/or static blocks (if any), which is executed from top to bottom in a class and from parent to child in the class hierarchy.
Why to use OpenCart Website Development platform for Ecommerce?